Canada’s Top Resistance Spot Welding Company
Resistance spot welding is a process where heat from electrical resistance is used with force and time to weld metallic materials. The concentration of pressure and electricity in a small “spot” causes the two sheets of metal directly between the caps (seen above) to melt into a molten state. Once cooled, these sheets have been “spot” welded together. This process can be controlled to produce individual spot welds, or in a line (Seam Welding).
Resistance welding’s primary use is in the manufacture of automobiles, where the average car has some 5,000 spot welds. The rise of coated steels, high strength steels, and most recently hot stamped steels and aluminum in the automotive industry have presented challenges to this simple but effective joining method. Huys has over thirty-five years’ experience in resistance spot welding (RSW) and has developed effective solutions to these challenges with the help of SORPAS. These include our patented or patent pending TiCaps™, and Taper Tools™.
Huys employees serve on committees of the American Welding Society (AWS), Standards Council of Canada (SCC) as well as ISO committees for RSW. Huys has numerous patents and patents pending for advances in RSW and related technologies.
Applications of Resistance Spot Welding Services
As a leading resistance spot welding company in Canada, Huys specializes in RSW solutions for various industries, particularly the automotive sector. On average, each car contains about 5,000 spot welds, making RSW essential in vehicle production. However, advances in coated and high-strength steels, along with the use of aluminum, have presented challenges in traditional spot welding. These innovations require specialized resistance spot welding services to achieve the strength and quality needed for automotive and industrial applications.
Innovations and Expertise at Huys: A Top Resistance Spot Welding Company
Huys has over 35 years of experience in RSW, working continuously to address new challenges in the field. As part of its resistance spot welding services, Huys has developed patented solutions like TiCaps™ and Taper Tools™, designed to improve weld quality and performance on complex materials like hot-stamped steels and aluminum. Additionally, Huys’ involvement with industry standards through the American Welding Society (AWS), the Standards Council of Canada (SCC), and ISO committees further enhances its leadership as a resistance spot welding company.
Why Choose Huys for Your Resistance Spot Welding Services?
With a focus on innovation, reliability, and compliance with industry standards, Huys is recognized as one of the best resistance spot welding companies in Canada. Our resistance spot welding services offer precise, high-quality welds tailored to the specific needs of the automotive and manufacturing sectors. For more information, explore our full range of services and solutions in resistance spot welding.
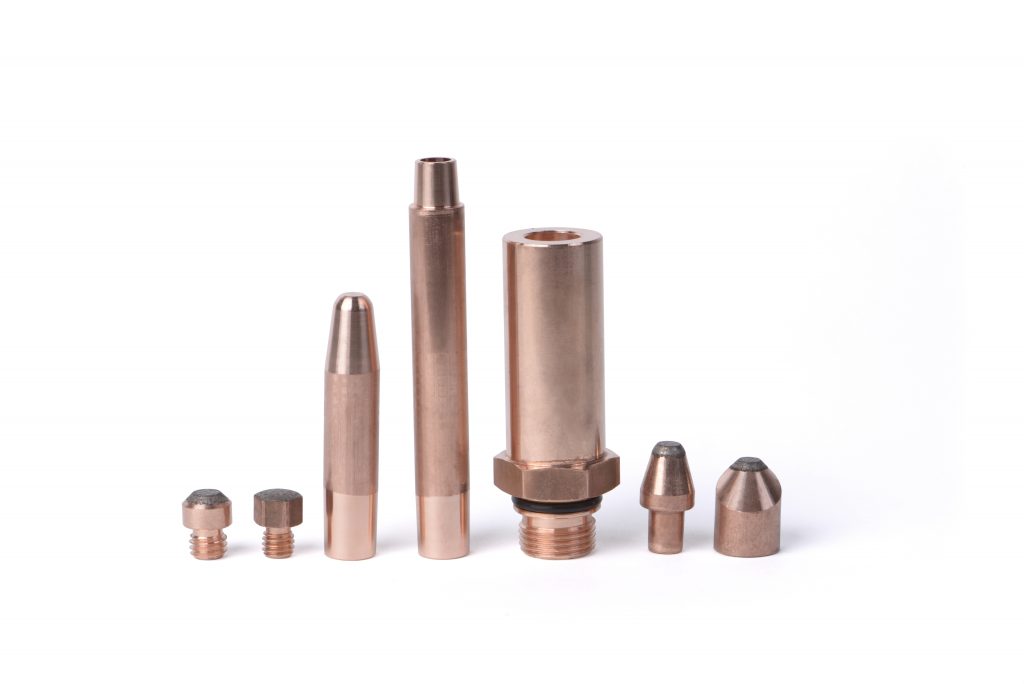


Electrode Holders Barrels and Bases

Honing: Taper Tool™

Projection Grounding Block Electrodes

Resistance Welding Alloys

Resistance Welding Caps/Tips

Resistance Welding Maintenance Tools

Shanks and Adaptors

Shunts and Cables

Spot Welding Electrodes

TiCaps™

Welding Accessories

Harms & Wende Weld Controllers

HWH Service and Repair
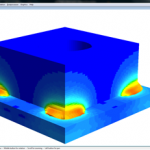
SORPAS® FEA Weld Simulation

Electrode Redressing



